Voltage Regulation of a Transformer and Its Influencing Factors
1. Introduction:
Transformers are essential components in power systems, primarily serving to convert voltage levels through electromagnetic induction to meet varying power demands. The voltage regulation of a transformer is a critical performance indicator that impacts both the stability of the power system and the safety and efficiency of electrical equipment. This article will examine the concept of transformer voltage regulation and the factors that influence it.
2. Definition of Voltage Regulation
Voltage regulation (VR) refers to the variation in the secondary voltage of a transformer between no-load and full-load conditions. It is typically expressed as a percentage and calculated using the following formula:
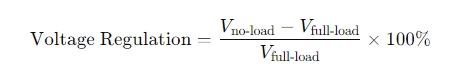
Where Vno-loadis the secondary voltage at no load, and Vfull-loadis the secondary voltage at full load. A smaller voltage regulation indicates a more stable voltage output from the transformer, reflecting better performance.

3. Key Factors Influencing Voltage Regulation
3.1 Load Types
Different types of loads affect transformer voltage regulation in distinct ways. Loads are generally categorized as resistive, inductive, or capacitive.
- Resistive Load: In the case of purely resistive loads, voltage regulation is relatively low, leading to minimal voltage fluctuations.
- Inductive Load: In an inductive load, the current lags behind the voltage. This lagging current, combined with the induced electromotive force, results in a drop in the secondary voltage, which in turn increases the voltage regulation.
- Capacitive Load: Capacitive loads cause the current to lead the voltage, which can result in an increase in the secondary voltage, thereby affecting voltage regulation.
3.2 Load Power Factor
The power factor of a load significantly influences voltage regulation. Power factor is defined as the ratio of real power to apparent power, and it measures how effectively the load utilizes electrical energy.
- A high power factor load indicates that the power factor is elevated, resulting in low voltage regulation and ensuring good voltage stability.
- Low Power Factor Load: As the power factor decreases, the current in the transformer increases, resulting in a greater voltage drop and higher voltage regulation.
3.3 Transformer Impedance
The impedance of a transformer, which consists of leakage reactance and winding resistance, directly affects voltage drops.
- Leakage Reactance: This refers to the impedance caused by leakage flux between the primary and secondary windings. A higher leakage reactance results in a greater voltage drop under load, which leads to increased voltage regulation.
- Winding Resistance: A higher winding resistance results in a larger voltage drop, which in turn increases voltage regulation. Therefore, the materials and design of the transformer have a direct impact on its voltage regulation.
3.4 Load Size
Voltage regulation varies with different load sizes. As the load increases, voltage regulation typically becomes larger because the increase in load current leads to more significant internal voltage drops.
3.5 Transformer Design and Structure
The design and structure of a transformer significantly influence its voltage regulation. Optimizing core materials, improving winding configurations, and minimizing leakage flux can enhance voltage regulation. Furthermore, matching inductances and selecting the appropriate number of winding turns contribute to improved voltage regulation.

MULTI-WINDING PHASE-SHIFTED RECTIFIER OVDT TRANSFORMER
4. Other Factors
In addition to the primary factors mentioned, environmental temperature, frequency variations, and load fluctuations can also influence voltage regulation. For example, a transformer operating at high temperatures may experience increased winding resistance, leading to larger voltage drops and elevated voltage regulation. Changes in frequency also affect the induced electromotive force, thereby impacting voltage regulation.
5. Conclusion
Transformer voltage regulation is a critical indicator of operational performance and stability. By analyzing factors such as load type, power factor, transformer impedance, load size, and transformer design, we can effectively predict and manage voltage regulation. Understanding these factors is essential for ensuring stable operation in power systems and for selecting the appropriate transformer.
In conclusion, by implementing proper design and optimizing operating conditions, voltage regulation in transformers can be minimized, thereby enhancing overall efficiency and safety in power systems.
1250kVA oil immersed transformer price
1600kVA oil immersed transformer
FR4 Machined Parts
1250kVA oil immersed transformer
Filament Wound Epoxy Tube
- more+releated article
- 2026-02-281250kVA Oil-Immersed Transformer Price and Cos
- 2026-02-27Detailed Explanation of FR4 Machined Parts Mac
- 2026-02-27Custom 1600kVA Oil Immersed Transformer Manufa
- 2026-02-26Precision FR4 Machined Parts for Electrical In
- 2026-02-26High-Quality Industrial 1250kVA Oil-Immersed T
- 2026-02-25Why is Filament Wound Epoxy Tube More Expensiv
- 2026-02-25XUJUE ELECTRICAL Officially Resumes Operations
- 2026-02-25Solar Duty Transformer: Sizing Challenges, Inv
- 2026-02-11Ztelecgroup Annual Gala Successfully Held
- 2026-02-10G10 epoxy board in the insulation parts of ele





