What is phenolic material, uses and characteristics
2024-09-25 14:47 | By: ZTELEC-www.ztelecgroup.com | 179click
1.What is phenolic?
Phenolic refers to a group of chemical compounds that are characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. These compounds are known as phenols.
Here are some common contexts in which "phenolic" is used:
Phenolic Compounds (Chemistry):
Phenolic compounds are a class of organic molecules that include a phenol group. Phenol itself is the simplest phenolic compound, with the chemical formula C₆H₅OH. These compounds are found naturally in plants and are known for their antioxidant properties. They play a role in the flavor, color, and resistance of plants to pathogens.
Phenolic Resins (Materials Science):
Phenolic resins are a type of synthetic polymer made from phenol and formaldehyde. These resins are widely used in the production of molded products, coatings, adhesives, and laminates due to their high mechanical strength, heat resistance, and insulation properties. They are commonly used in electrical components, automotive parts, and kitchenware.
Phenolic Plastics:
Phenolic plastics, also known as Bakelite, are made from phenolic resins and are known for their durability and resistance to heat, chemicals, and electricity. They were some of the first synthetic plastics developed and are still used in various applications where high strength and heat resistance are required.
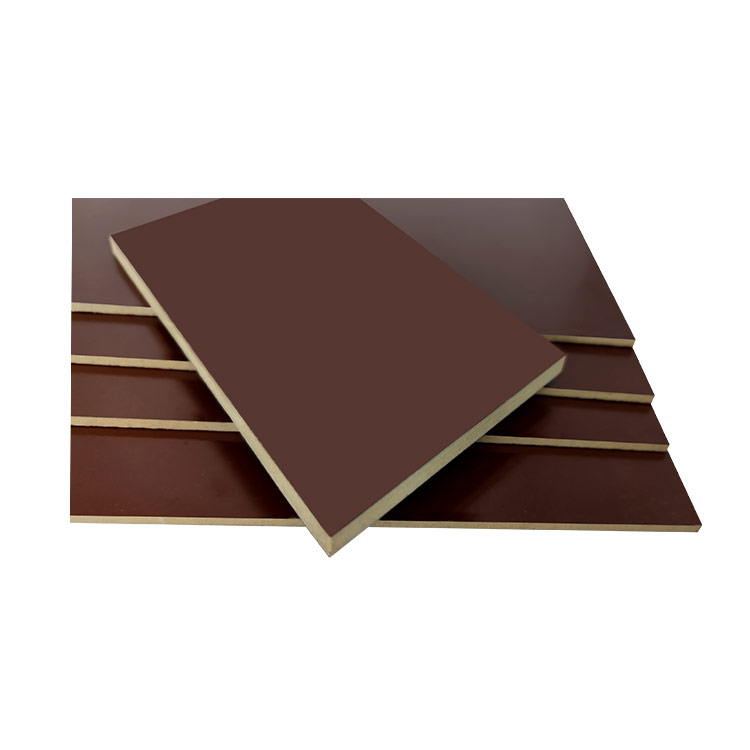
2.What are the uses of phenols
Phenols, a group of organic compounds characterized by a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to an aromatic ring, have a wide range of uses across various industries due to their chemical properties. Here are some of the most common uses of phenols:
Plastic and Resin Manufacturing
Phenolic Resins: Phenols are used to produce phenolic resins, which are employed in the manufacture of various plastics, laminates, and adhesives. These resins are known for their high heat resistance and mechanical strength, making them suitable for electrical insulators, automotive parts, and kitchenware.
Chemical Industry
Intermediate in Chemical Synthesis: Phenols are important intermediates in the synthesis of various chemicals, including bisphenol A (BPA), which is used in the production of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins.
Production of Dyes and Explosives: Phenol derivatives are used in the production of certain dyes, such as azo dyes, and in the synthesis of explosives like picric acid.
Textile Industry
Dyeing and Printing: Phenolic compounds are used in the textile industry for dyeing and printing fabrics, as they can bind well with fibers and provide vibrant, long-lasting colors.

3.Benefits of Phenolic Sheet
Phenolic sheets, also known as phenolic laminates, are composite materials made from phenolic resin impregnated into layers of paper, fabric, or glass cloth under heat and pressure. These sheets are known for their excellent mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties, making them highly versatile in various industrial and commercial applications. Here are some of the key benefits of phenolic sheets:
1. High Mechanical Strength
Durability: Phenolic sheets have high tensile, compressive, and flexural strength, making them durable and resistant to mechanical stresses. They are often used in applications where structural integrity is critical.
Impact Resistance: They exhibit good impact resistance, which helps them withstand physical impacts without cracking or breaking.
2. Excellent Heat Resistance
Thermal Stability: Phenolic sheets can withstand high temperatures without losing their mechanical properties. This makes them suitable for applications in environments with elevated temperatures, such as electrical insulation and engine components.
Low Thermal Expansion: They have a low coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning they do not expand or contract significantly with temperature changes, ensuring dimensional stability.
3. Electrical Insulation
Dielectric Properties: Phenolic sheets are excellent electrical insulators, making them ideal for use in electrical and electronic applications. They prevent electrical conduction, reducing the risk of short circuits and electrical failures.
Arc Resistance: These sheets can resist electrical arcing, which is crucial in high-voltage applications where arcing could otherwise cause damage or fire.
4. Chemical Resistance
Corrosion Resistance: Phenolic sheets are resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, solvents, and oils. This makes them suitable for use in chemical processing plants, laboratories, and environments where exposure to corrosive substances is common.
Moisture Resistance: They are also resistant to moisture, which prevents degradation and swelling when exposed to water or humidity.
5. Fire Resistance
Flame Retardant: Phenolic sheets are inherently flame retardant and self-extinguishing. They do not easily catch fire, and when they do, they produce minimal smoke and toxic fumes. This property is particularly valuable in construction, transportation, and other safety-critical applications.
6. Dimensional Stability
Precision Machining: Phenolic sheets can be precisely machined to tight tolerances without warping or deforming, ensuring that they maintain their shape and size over time.
Low Shrinkage: These sheets exhibit low shrinkage during processing, which contributes to their dimensional stability in finished products.
7. Ease of Fabrication
Workability: Phenolic sheets can be easily cut, drilled, punched, and machined into various shapes and sizes, making them versatile for different manufacturing processes.
Surface Finish: They can be produced with smooth, glossy surfaces or textured finishes, depending on the application requirements.
8. Versatility
Variety of Grades: Phenolic sheets are available in different grades, including paper-based, fabric-based, and glass cloth-based laminates, each offering specific properties tailored to particular applications.
Wide Range of Applications: They are used in a broad spectrum of industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, marine, construction, and more.
9. Cost-Effectiveness
Long Lifespan: The durability and resistance of phenolic sheets to various environmental factors contribute to a long service life, reducing the need for frequent replacements and lowering overall maintenance costs.
Material Efficiency: The ability to precisely machine and fabricate phenolic sheets reduces material waste, contributing to cost savings in production.
In summary, phenolic sheets offer a combination of strength, heat resistance, electrical insulation, chemical resistance, and fire retardancy, making them highly beneficial in demanding environments where reliability and safety are paramount.
tags:insulation failure transformertransformer short circuittransformer overheatingtransformer overloadtransformer maintenance
- more+releated article
- 2026-01-04Common Power Transformer Faults: Causes, Solut
- 2025-12-312026 New Year Holiday Notice
- 2025-12-31Operation, Maintenance, and Service Life Manag
- 2025-12-30How to Select a 100 kVA–500 kVA Distribution
- 2025-12-29The Impact of NHN NMN Composite Insulation on
- 2025-12-26Practical Application of GPO-3 Insulation Boar
- 2025-12-2510kV Transformer Replacement Timeline: Install
- 2025-12-25Low Smoke EN45545 GPO3 UPGM203 Laminated Board
- 2025-12-24Merry Christmas — ZTelecgroup Christmas Cele
- 2025-12-24How to Select a Suitable 50kVA–500kVA Distri





