3240 Fiberglass Sheet vs. FR4: Key Differences and Selection Guide
In the fields of industrial insulation and electronic substrates, 3240 fiberglass sheet and FR4 fiberglass sheet are two widely used yet distinctly different materials. Their differences in material composition, performance characteristics, and application scenarios have a direct impact on material selection decisions across various projects. In this guide, we’ll break down the main distinctions between the two and offer practical advice to help you choose the right material for your specific application.
Material Composition
3240 is made with a paper- or fabric-based reinforcement structure, combined with phenolic or epoxy resin. It typically appears in yellow, with some red or black variants. It is rated Class B for thermal resistance. While 3240 offers relatively high mechanical strength, it is susceptible to deformation under humid conditions, and its density usually does not exceed 1.9 g/cm³.
FR4 uses woven fiberglass cloth as the reinforcement material and is cured with pure epoxy resin. It is primarily green in color, with some black or yellow versions available. FR4 has a broader thermal resistance range and a stable density around 1.85 g/cm³, and exhibits superior impact resistance and dimensional stability.
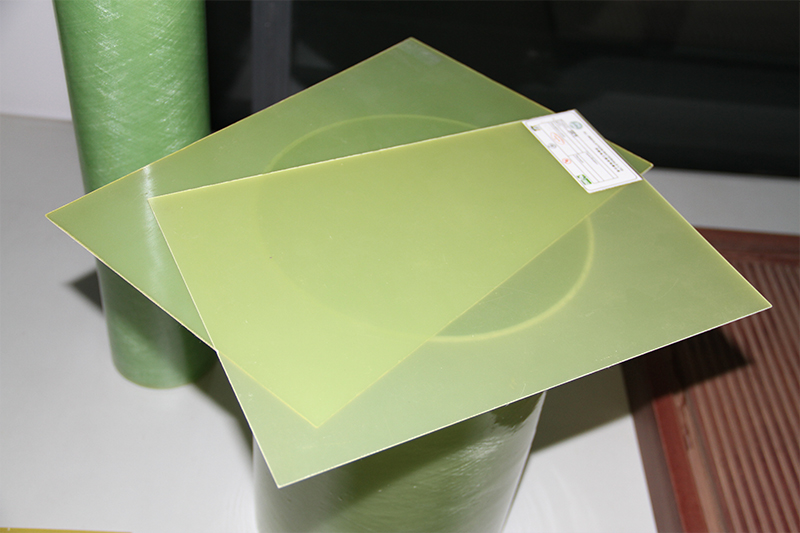
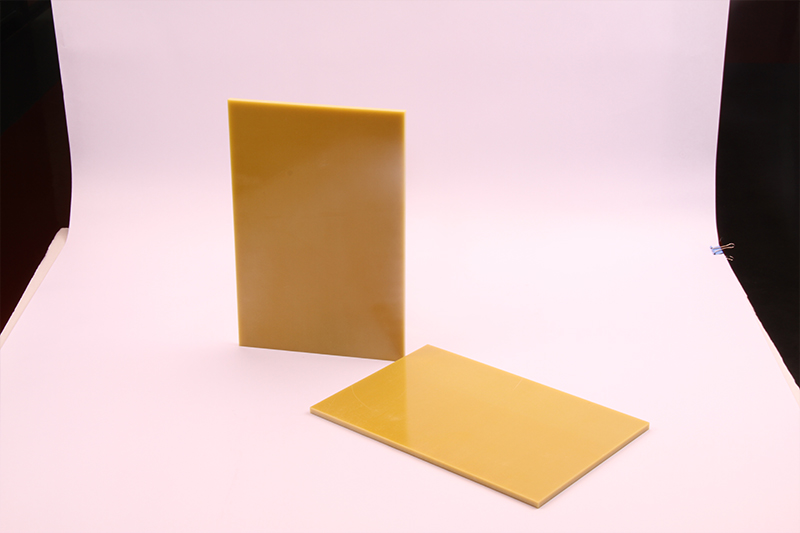

Performance Comparison
In terms of insulation performance, 3240 fiberglass sheet provides adequate insulation for general electrical equipment, with compliant insulation resistance levels. FR4, on the other hand, is preferred for high-frequency applications such as 5G communication devices, thanks to its low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor.
In terms of flame retardancy, FR4 meets the UL94 V-0 flame-retardant standard, meaning it is self-extinguishing when exposed to fire. 3240 has no defined flame-retardant rating, and some halogen-containing formulations may fail to meet modern environmental standards.
Application Scenario Comparison
1. Suitable Applications for 3240 Fiberglass Sheet
Mechanical Equipment Insulation:
3240 fiberglass sheet is suitable for use as gaskets in transformer oil environments and as insulating structural components in distribution boxes. It is especially valued for its low cost and ease of manual processing.
General Electrical Applications:
It can be used as a non-critical insulating component in motors and electrical equipment, especially in scenarios where high-temperature resistance is not a primary concern.
Budget-Sensitive Projects:
When basic performance requirements are met, 3240 fiberglass sheet offers excellent cost-effectiveness, making it a practical choice for cost-conscious applications.
2. Suitable Applications for FR4 Fiberglass Sheet
High-End Electronic Devices:
FR4 is the ideal base material for multilayer PCBs and high-frequency circuit boards. Its low signal loss characteristics significantly improve signal transmission efficiency.
Demanding Environments:
FR4 fiberglass sheet is widely used in chemical automation systems, rail transit power systems, and other harsh environments, thanks to its ability to withstand high temperatures, corrosive atmospheres, and flame exposure.
Precision Manufacturing:
Due to its tight thickness tolerance, FR4 is suitable for CNC-machined high-precision sensor circuit boards, precision planetary gears, and other components that require exact dimensions.

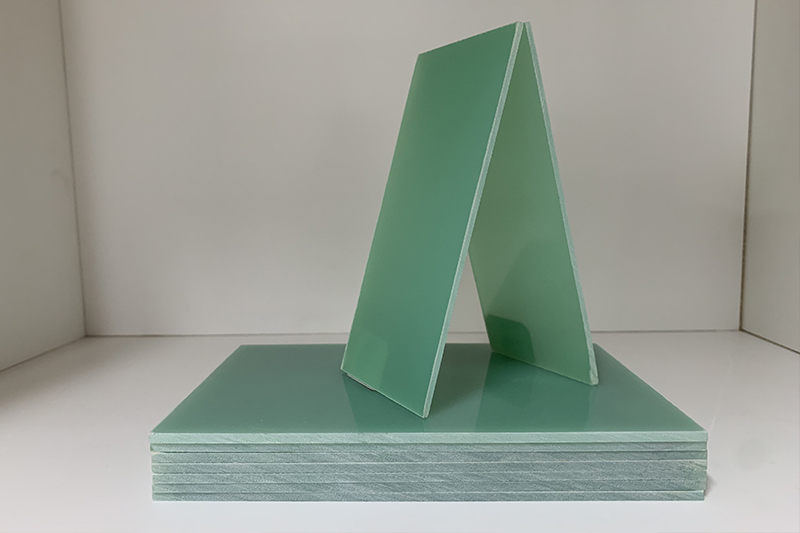
Key Performance Verification Points and Material Selection Pitfalls
1. Heat Resistance Testing
3240 fiberglass sheet may experience a decline in mechanical properties—such as brittleness or deformation—when exposed to temperatures above 155°C. In contrast, FR4 fiberglass sheet remains stable even at 180°C.
If the equipment operates continuously above 150°C—for example, near high-temperature ovens—3240 should be avoided, as it may lead to insulation failure or structural damage.
2. Flame Retardancy Verification
FR4 fiberglass sheet meets UL94 V-0 flame-retardant standards, making it suitable for use in fire-critical areas such as data centers and public buildings.
On the other hand, 3240 fiberglass sheet does not have a certified flame-retardant rating, and using it in fire-prone environments may pose serious safety risks.
3. Environmental Compliance
Some 3240 fiberglass products contain halogens, such as brominated flame retardants, which do not comply with the EU RoHS directive. When it is used as an export products, we must select carefully.
FR4 fiberglass sheet is available in halogen-free formulations and can pass environmental certifications from organizations like SGS, helping users mitigate compliance risks more effectively.
1250kVA oil immersed transformer price
1600kVA oil immersed transformer
FR4 Machined Parts
1250kVA oil immersed transformer
Filament Wound Epoxy Tube
- more+releated article
- 2026-02-281250kVA Oil-Immersed Transformer Price and Cos
- 2026-02-27Detailed Explanation of FR4 Machined Parts Mac
- 2026-02-27Custom 1600kVA Oil Immersed Transformer Manufa
- 2026-02-26Precision FR4 Machined Parts for Electrical In
- 2026-02-26High-Quality Industrial 1250kVA Oil-Immersed T
- 2026-02-25Why is Filament Wound Epoxy Tube More Expensiv
- 2026-02-25XUJUE ELECTRICAL Officially Resumes Operations
- 2026-02-25Solar Duty Transformer: Sizing Challenges, Inv
- 2026-02-11Ztelecgroup Annual Gala Successfully Held
- 2026-02-10G10 epoxy board in the insulation parts of ele





